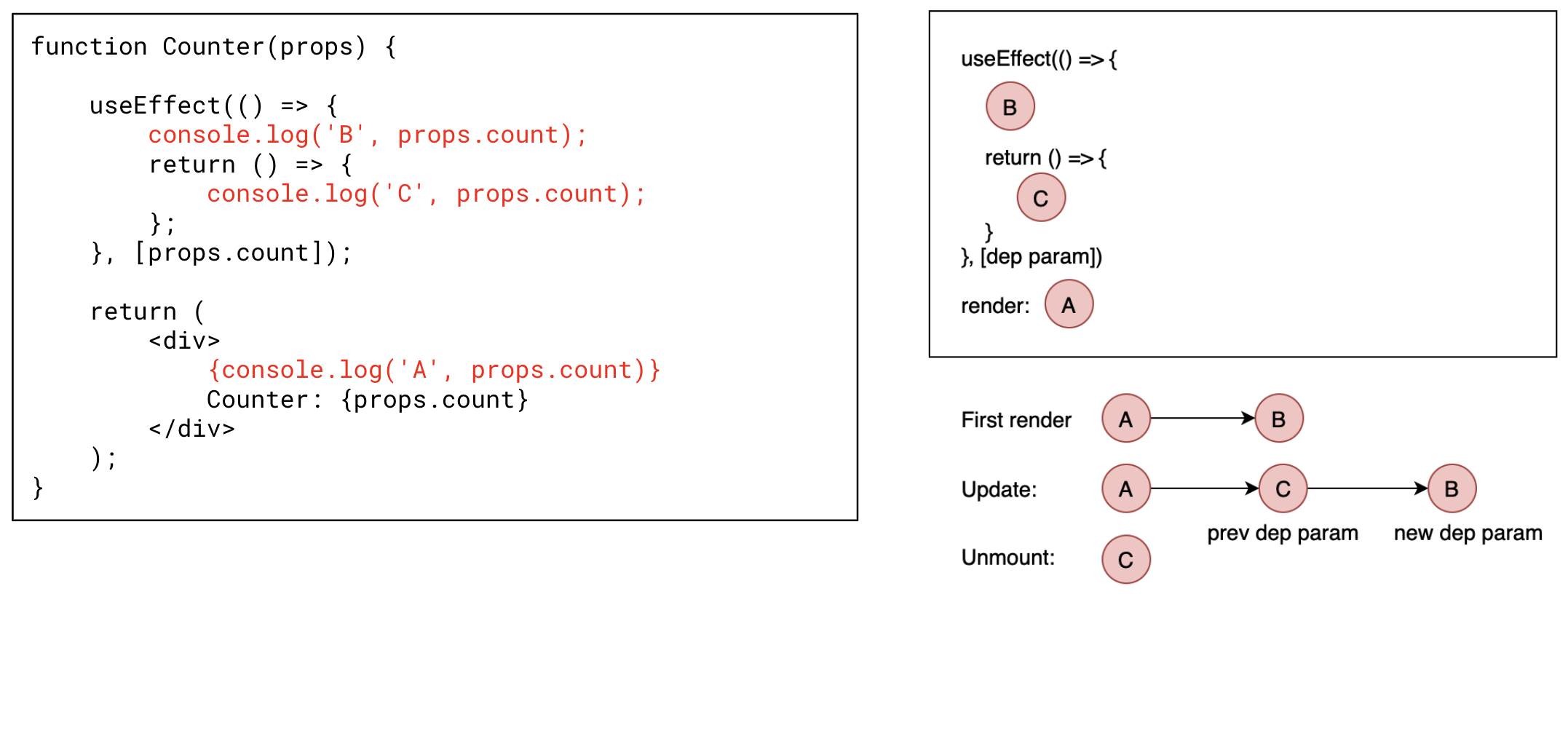
React useEffect 的渲染/更新/卸载顺序?

React.memoconst MyComponent = React.memo(function MyComponent(props) {
/* render using props */
});
React.memo is a higher order component. It's similar to React.PureComponent but for function components instead of classes.
If your function component renders the same result given the same props, you can wrap it in a call to React.memo for a performance boost in some cases by memoizing the result. This means that React will skip rendering the component, and reuse the last rendered result.
By default it will only shallowly compare complex objects in the props object. If you want control over the comparison, you can also provide a custom comparison function as the second argument.
DOM 是 JavaScript 操作网页的接口,全称为“文档对象模型”(Document Object Model)。它的作用是将网页转为一个 JavaScript 对象,从而可以用脚本进行各种操作(比如增删内容)。
浏览器会根据 DOM 模型,将结构化文档(比如 HTML 和 XML)解析成一系列的节点,再由这些节点组成一个树状结构(DOM Tree)。所有的节点和最终的树状结构,都有规范的对外接口。
DOM 只是一个接口规范,可以用各种语言实现。所以严格地说,DOM 不是 JavaScript 语法的一部分,但是 DOM 操作是 JavaScript 最常见的任务,离开了 DOM,JavaScript 就无法控制网页。另一方面,JavaScript 也是最常用于 DOM 操作的语言。后面介绍的就是 JavaScript 对 DOM 标准的实现和用法。
Portal 中文即“传送门”的意思,来看一张电影剧照,不用多说,你应该能猜出来是什么意思:
官方定义:Portals 提供了一种很好的将子节点渲染到父组件以外的 DOM 节点的方式。
ReactDOM.createPortal(child, container);
Context 通过组件树提供了一个传递数据的方法,从而避免了在每一个层级手动的传递 props 属性。在一个典型的 React 应用中,数据是通过 props 属性由上向下(由父及子)的进行传递的,但这对于某些类型的属性而言是极其繁琐的(例如:地区偏好,UI 主题),这是应用程序中许多组件都所需要的。 Context 提供了一种在组件之间共享此类值的方式,而不必通过组件树的每个层级显式地传递 props 。